In this exercise we are going to explore the two primary means of positioning elements using CSS.
Floats
From the W3C
A float is a box that is shifted to the left or right on the current line. The most interesting characteristic of a float (or “floated” or “floating” box) is that content may flow along its side (or be prohibited from doing so by the “clear” property). Content flows down the right side of a left-floated box and down the left side of a right-floated box.
A Few Examples
More on Floats
Lab Problems
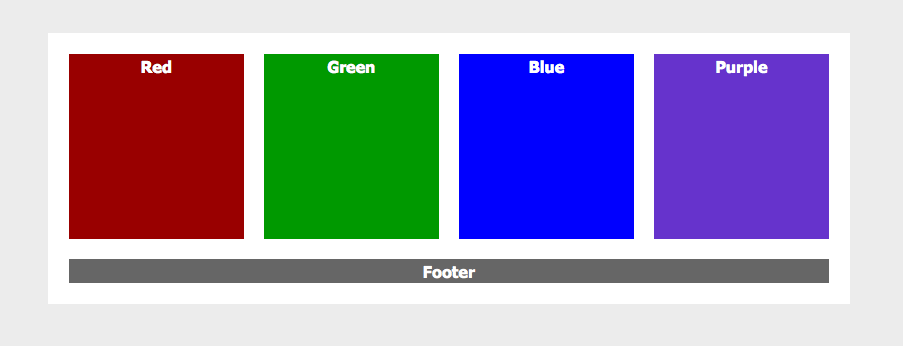
Please try and recreate the screenshots below using floats.
Float Example One
Float Example 2
Absolute Positioning
Absolute positioning allows you to position an element relative to it’s nearest positioned parent element. If no such parent element exists then the html or body element is used (depending on the browser).
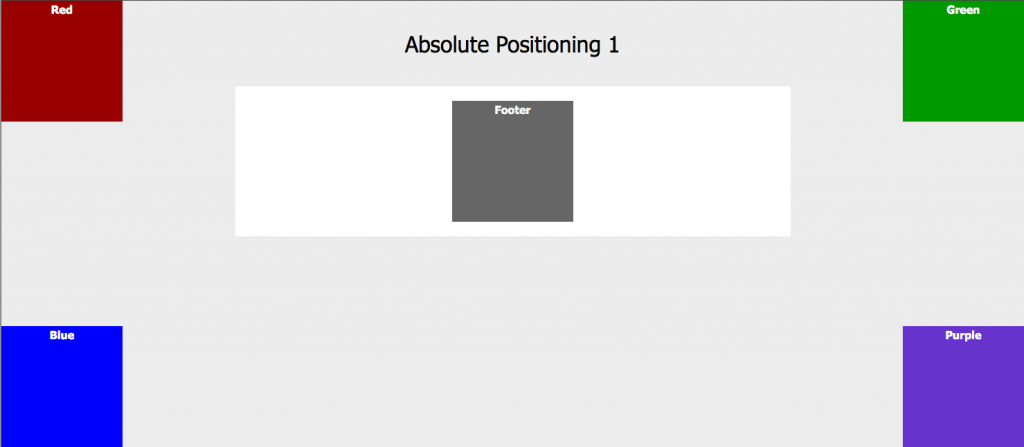
Lab Problems
Please try and recreate the screenshots below using floats.